Multicopter Flight Modes
Multicopter Flight Modes
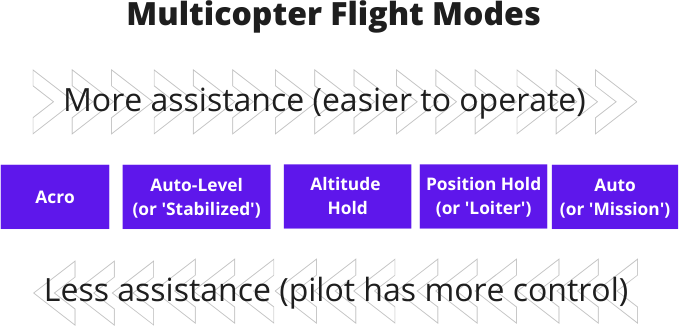
Multicopters are equipped with an onboard computer called a flight controller , which utilizes information from various onboard sensors to help the pilot fly the aircraft in a stable and controlled manner. The flight controller offers various flight modes that provide varying degrees of flight automation. Some modes provide more control to the pilot but are more demanding to operate, while others offer increased levels of flight stabilization and automation. The diagram below illustrates some of the most commonly used flight modes, although different platforms may provide a broader range of options.
-
The Position Hold (sometimes called 'Loiter') mode is the easiest mode to fly. The pilot can control the speed of the aircraft in any direction using the sticks, and if they let go of the sticks, the aircraft will automatically stop and maintain its current location and altitude. This feature requires an advanced flight controller with GPS, to enable this level of stabilization.
-
In Auto-Level (sometimes called 'Angle' or 'Horizon') mode the pilot uses the right stick of the controller to adjust the tilt angle of the drone, and when the stick is released, the drone automatically returns to a level orientation—hence the name Auto-Level. However, while the aircraft levels itself, it will continue drifting in its previous direction of movement, and will not hold its current position automatically. The aircraft does not hold its altitude either, as it does in Position Hold mode. It is up to the pilot to continuously adjust the throttle input in order to maintain the altitude and avoid crashing with the ground. This in itself can be quite challenging for novice pilots.
-
In the Stabilized (also called 'Acro' or 'Rate') flight mode , the pilot controls the drone's rotation using the right stick, and when the stick is released, the drone maintains its current orientation rather than leveling itself. Like Auto-Level, it does not hold the altitude and it is up to the pilot to continuously adjust the throttle to hold the altitude. This mode is significantly more challenging than Auto-Level but provides unparalleled control, making it the preferred choice for expert FPV drone racers seeking precision and agility.
FPV Racing Flight Modes
FPV racing drones require exceptional agility and maneuvering precision, so they are typically are designed to use flight modes that give pilots maximum level of control: the Stabilized and Auto-Level modes. To achieve this, they are equipped with simpler, lighter manual flight controllers that prioritize responsiveness over autonomy, which means they lack the sensors and features necessary for Position Hold or Auto flight modes. However, some beginner-friendly FPV racing drones such as the DJI FPV drone do include position hold functionality.
For this course, we will learn to fly the vehicle using Position Hold. Advanced users which want to learn to fly in Auto-Level or Acro modes can do so by changing the flight mode within the simulation.